Suez canal the miracle canal
The Suez Canal: A Lifeline of Global Maritime Trade
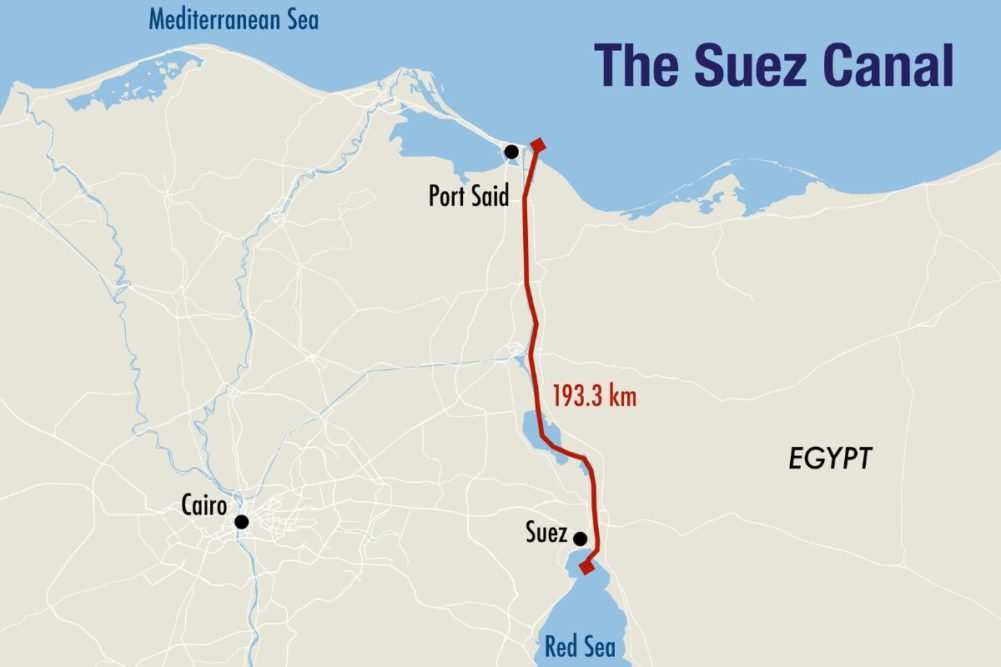
The Suez Canal, a man-made waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, is a marvel of engineering and a critical artery for global maritime trade. This ambitious project, undertaken by the Egyptian government, has transformed the landscape of international commerce and transportation.
The Birth of a Visionary Idea
The concept of a canal connecting the Mediterranean and Red Seas dates back to ancient times, with various attempts made by the Pharaohs, the Romans, and the Caliphs of the Middle Ages. However, it was not until the 19th century that the idea gained traction and was finally realized.In 1854, the Egyptian government, under the rule of Khedive Said, granted a concession to the French engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps to construct the Suez Canal. After years of arduous work and overcoming numerous challenges, the canal was officially opened in 1869, marking a significant milestone in the history of global transportation.
The Suez Canal's Strategic Importance
The Suez Canal has become a vital link in the global supply chain, allowing ships to bypass the lengthy journey around the Cape of Good Hope. This strategic location has made the canal a crucial chokepoint, with an estimated 12% of global trade passing through its waters.The canal's importance extends beyond its economic significance. It has also played a crucial role in geopolitics, with various conflicts and disputes erupting over its control throughout history. The Suez Crisis of 1956, when Egypt nationalized the canal, is a prime example of the strategic importance of this waterway.
Continuous Expansion and Modernization
To keep pace with the growing demands of global trade, the Suez Canal has undergone several expansion and modernization projects over the years. In 2015, the Egyptian government completed a major expansion project, which included the construction of a new 35-kilometer-long parallel channel, allowing for two-way traffic and reducing transit times.The canal's infrastructure has also been continuously upgraded, with the introduction of modern navigation systems, dredging operations, and the deployment of a fleet of high-tech tugboats to assist in the passage of ships.
The Suez Canal's Impact on Global Trade
The Suez Canal's impact on global trade cannot be overstated. It has significantly reduced the time and cost of maritime transportation, allowing for the efficient movement of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa. This, in turn, has facilitated the growth of international trade, contributing to the global economy's prosperity.Moreover, the canal's strategic location has made it a hub for various industries, including shipping, logistics, and energy. The development of port facilities and related infrastructure around the canal has further reinforced its importance as a crucial node in the global supply chain.
Challenges and the Future of the Suez Canal
Despite its immense success, the Suez Canal faces ongoing challenges, such as the threat of climate change, the potential for geopolitical tensions, and the need for continuous investment in infrastructure and technology.As the world grapples with the transition to a more sustainable future, the Suez Canal's role in facilitating global trade will continue to be scrutinized. The Egyptian government and the Suez Canal Authority are actively exploring ways to reduce the canal's environmental impact and ensure its long-term viability.In conclusion, the Suez Canal stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the power of ambitious infrastructure projects. As a vital artery of global maritime trade, the canal has transformed the landscape of international commerce and transportation, cementing its place as a true marvel of the modern world.